Successful products rely on a good understanding of how users behave and why choose in specific ways. Approaching systematically to product design thus leads to better diagnosis, which in turn leads to better-designed solutions.
All habits or behaviors proceed through four stages, always in the same order:
- Cue triggers our brains to start behavior. It’s the bit of information that predicts a reward.
- Motivation without some level of motivation, we have no reason to act. Craving is the motivational force behind every action.
- Action is the actual response that you want to your user perform. Whether the action occurs or not depends on how motivated the user is and how much friction is associated with the behavior.
- Rewards are the end goal of every action.
The cue is about noticing the reward. The motivation is about wanting the reward. The action is about obtaining the reward. We chase rewards because they satisfy us and teach us.
Eliminate the cue, and your habit will never start. Reduce the craving, and you will not experience enough motivation to act. Make the behavior difficult, and you will not be able to do it. And if the reward fails to satisfy your needs, you will have no reason to do it again.
Without the first three steps, the behavior will not occur. Without all 4, the action will not be repeated.
Cue: Make it obvious
Our mind is continuously analyzing our internal and external environment for hints of where rewards are located. Because the cue is our first indicator that we are close to a reward.
Digital products are the environment we can control and create, as designers. It is supposed to be the place where we drop all these small things that make the user think there is a reward behind it.
Progress bars are a phenomenal tool to motivate people to complete a simple task, but it inhibits us from remembering what the task was once achieved. So, it will never be used if we want to take something away from that task (e.g.: education).
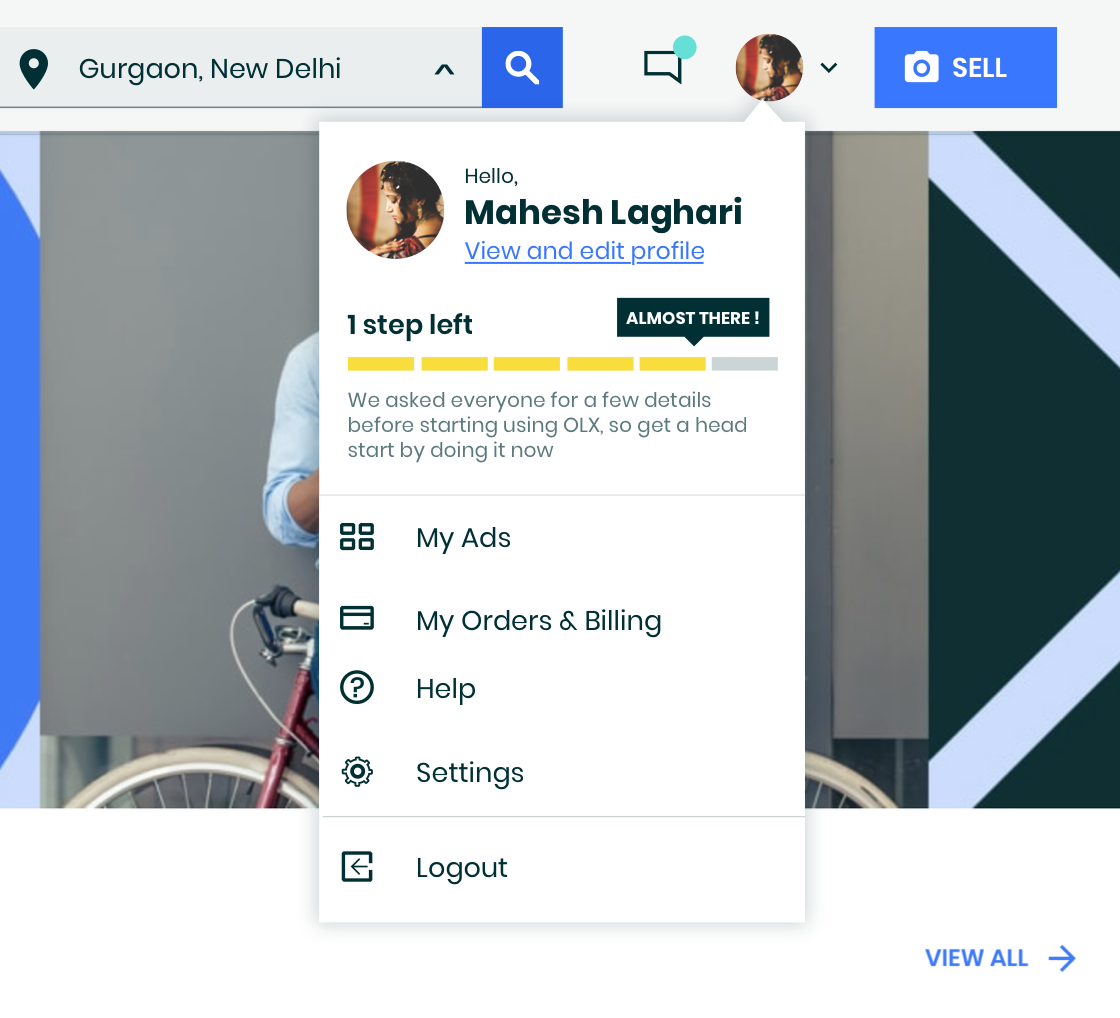
People remember uncompleted or interrupted tasks better than completed tasks. We are motivated to fill up progress bars because then we can alleviate that part of the mental energy we were using in this task.
“Our minds quickly forget the finished tasks. However, they are programmed to continually interrupt us with reminders of unfinished tasks” — Bluma Zeigarnik
In conclusion, Cues are meaningless until they are interpreted. The thoughts, feelings, and emotions of the observer are what transform a cue into a motivator. It naturally leads us to a craving.
Motivation: Make it attractive
Motivation differs from person to person. The same cues do not motivate all the people. There are different types of motivations. For every action, you have extrinsic or intrinsic motivation factors.
Extrinsic rewards drive extrinsic motivation. It could work in the short term, but it does not scale. Once you reach a certain level of extrinsic motivation, you start to need more of it. You are going to get a little less reward each time.
But the intrinsic rewards are much more powerful. We can keep happily working towards them without any damage. The big four are:
- Community refers to the feeling of belonging and being part of something bigger than just us.
- Meaning this is a goal that you choose for yourself because it means something to you your friends or your family. It is why thousands of people contribute to Wikipedia without getting paid. They have this sense that they should share this information with the world.
- Autonomy refers to the freedom that we are looking for all the time. The ability we have to make a choice. You are making your own choices with your way of working, at least.
- Mastery is continuously improving and seeing that you are growing yourself. Mastery is the reason why people can spend hours trying to play the piano.
We can, and we should create an environment for users to be able to get into the state of flow. We can create communities; we can create meaning. In the case of profile completion, we created the feeling of mastery that we have improved our OLX self by improving our profile.
Action: Make it easy
Action is the type of behavior that will deliver an outcome. Conventional wisdom says that motivation is the key for a behavior to happen, maybe if you want this enough, you will do it anyway.
But the truth is that our real motivation is to be lazy and to do what is convenient. It is human nature to follow the Law of Least Effort.
In this case, we managed complexity by using staged disclosure. Staged disclosure is a variant of progressive disclosure in which users step through a linear sequence of options, with a subset displayed at each step.
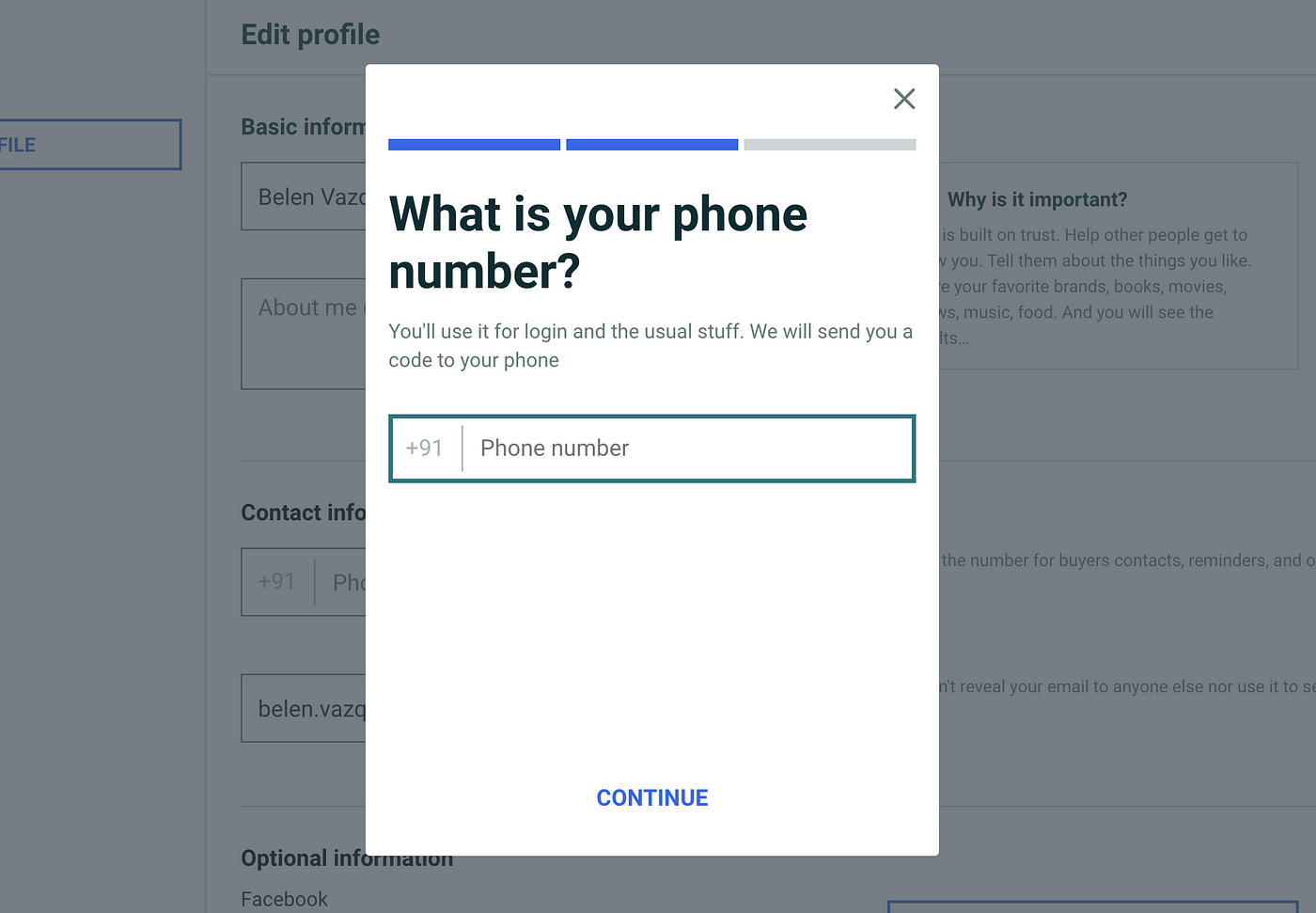
Staged disclosure is useful when you can divide a task into distinct steps that have little interaction. It is problematic when the levels are interdependent, and users must alternate between them.
Rewards: Make it satisfying
Reward systems are a powerful tool for designers to ensure that users get the most value out of their products. Digital products are not limited to using only one reward; they might use different delivery methods. These can be an excellent way for users to see the value in your product, adding a deeper level of engagement to your product as a result.
- Information reward. These are images, articles, and content delivered to users through a feed. We refresh app feeds in the hopes that we receive new information and content, much like how a slot machine either deals a jackpot or a bust.
- Social reward. We’re all vulnerable to social approval. Social rewards cater to three powerful emotions: vanity, self-worth, and validation.
- Gamification is scoring systems, achievements, and other game-like features in non-game apps.
- Monetization gives a physical product or money when users complete critical actions. Monetary rewards, when given without issue, are a great way to tap into power users and encourage the continued use of a product.
In this particular case, we worked with a different reward, since the craving was not intrinsic. The reward here was the mental alleviation of the brain energy that this task was taken from us.
Improving profile completeness has been a great way to personalize experiences and engage both buyers and sellers. The increase in the number of people who had completed their profile was huge, which supports the whole theory.
